Is Marburg Virus Zoonotic
Marburg hemorrhagic fever Marburg HF is a rare but severe hemorrhagic fever which affects both humans and non-human primates. A related virus is Marburg virus named after a city in Germany where a laboratory worker accidently infected himself and caused the first human case.
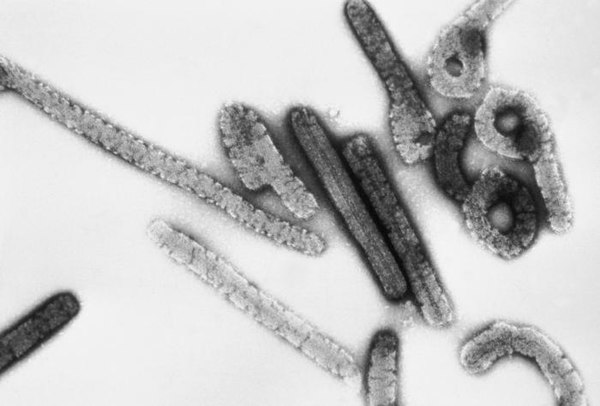
Marburg Virus Disease Wikiwand
Marburg and Ebola viruses are zoonotic pathogens members of the Filoviridae family which cause severe often fatal illness in humans.

Is marburg virus zoonotic. The initial human infection is acquired from wildlife and subsequent person-to-person spread propagates the outbreak until it is brought under control. Infection is suspected to result from contact between this reservoir and. Monkeys are susceptible to Marburg.
Marburg HF is caused by Marburg virus a genetically unique zoonotic or animal-borne RNA virus of the filovirus family. Marburg virus disease MVD describes a viral haemorrhagic fever responsible for a number of out-breaks across easternand southern Africa. Although it is unclear as to which animals contain both Marburg and Ebola it is thought that both may be transmitted to humans from monkeys andor bats African fruit bat and Rousettus bat.
Although from Germany and not a deep African jungle a Marburg virus still sounds like a vicious killer especially if said with a thick German accent. Both Marburg and Ebola virus diseases are zoonotic infections whose primary hosts are thought to be bats. The World Health Organization WHO rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen.
Marburg a highly infectious disease in the same family as the Ebola virus is transmitted from fruit bats and can be transmitted through humans via direct contact of the bodily fluids of infected people surfaces and materials. Transmission of Marburg virus predominantly occurs via close contact as well as via infected blood and other body fluids. Marburg virus disease was first identified during an outbreak in 1967 when laboratory workers in Marburg and Frankfurt Germany and Belgrade Yugoslavia what is now Serbia were infected with a previously unknown infectious agent.
Egyptian rousette bats ERBs are reservoir hosts for the Marburg virus MARV. This disease was named Marburg virus disease MVD after the West German town of Marburg an der Lahn where most human infections and deaths had been recorded. It is a zoonotic disease with the Egyptian rousette Rousettus aegyp-tiacus identified as a reservoir host.
It is a zoonotic disease with the Egyptian rousette Rousettus aegyptiacus identified as a reservoir host. MVD is a viral hemorrhagic fever VHF and the clinical symptoms are indistinguishable from Ebola virus disease EVD. Marburg virus disease MVD describes a viral haemorrhagic fever responsible for a number of outbreaks across eastern and southern Africa.
Marburg virus is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus genus MarburgvirusMarburg virus MARV causes Marburg virus disease in humans and other primates a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. Marburg virus is related to Ebola virus. Fruit bats Rousettus aegyptii are considered the natural host of the virus.
The five species of Ebola virus are the only other known members of the filovirus family. Marburg virus disease MVD. Formerly Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a severe illness of humans and non-human primates caused by either of the two marburgviruses Marburg virus MARV and Ravn virus RAVV.
The exact nature of the virus that the bats harbour is not known and these viruses may be much less pathogenic in humans compared to Ebola or Marburg virus outbreaks in. It is generally accepted that Marburg virus is a zoonotic animal borne virus. Both belong to the Filoviridae family of zoonotic viruses and cause outbreaks of hemorrhagic fevers with high fatality rates in humans and nonhuman primates.
It is unknown how Marburg virus first transmits from its animal host to humans. The immune dynamics and responses to MARV infection in ERBs are poorly understood and limited information exists on the role of antibodies in protection of ERBs against MARV infection. Marburg and Ebola viruses are considered to be zoonotic infections transmitted to humans from life cycles in other animals.
However for the 2 cases in tourists visiting Uganda in 2008 unprotected contact with infected bat feces or aerosols are the most likely routes of infection. After this initial crossover of virus from host animal to humans transmission occurs through person-to-person. The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous.
In computerized models of prior outbreaks in areas with known zoonotic viral reservoirs in Africa it is estimated that 22 million people are at risk from Ebolavirus infection and 105 million are potentially endangered by Marburg virus infection 45.

Geographic Distribution And Phylogenetic Analysis Of Marburg Virus A Download Scientific Diagram

Mean Duration Of The Igg Immune Response To Marburg Virus In Previously Download Scientific Diagram

Marburgvirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
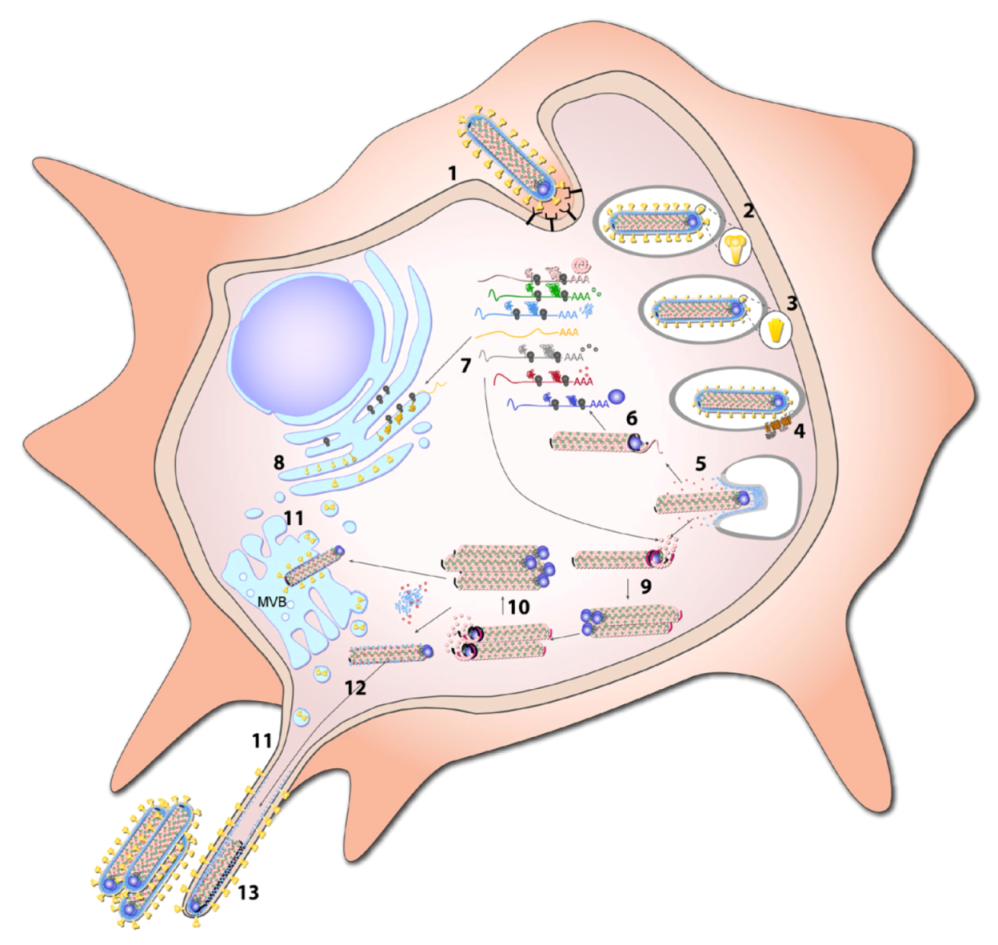
Viruses Free Full Text Forty Five Years Of Marburg Virus Research Html

Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Pathogenesis Model Download Scientific Diagram

Marburg Virus Disease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
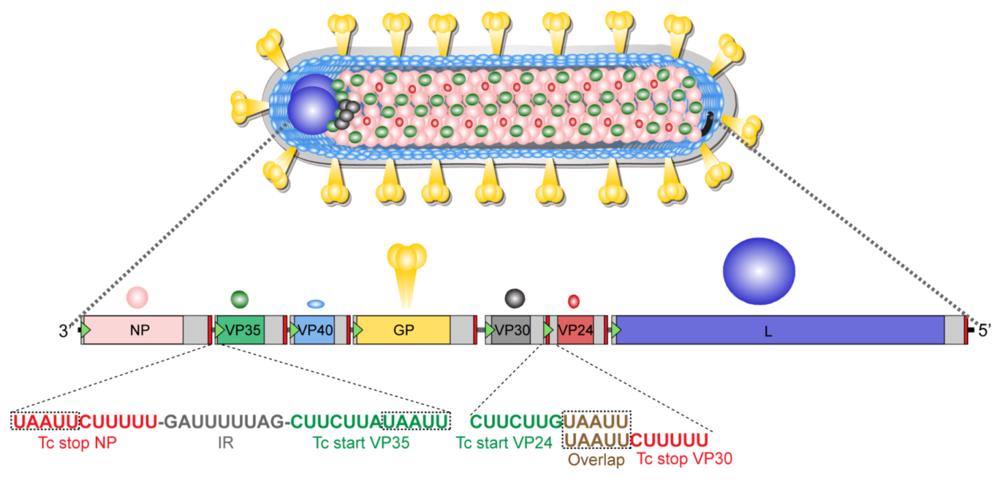
Viruses Free Full Text Forty Five Years Of Marburg Virus Research Html
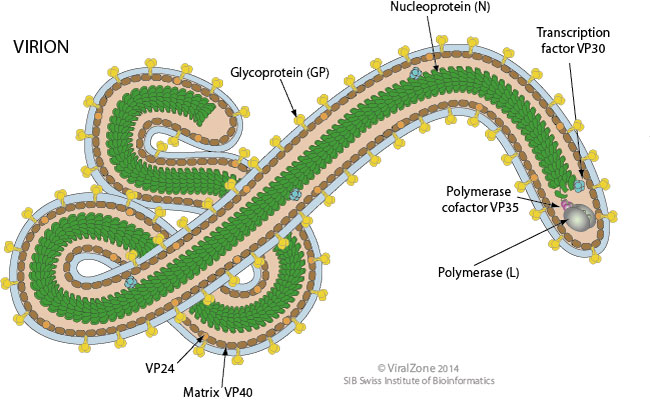
Marburg Virus Structure And Transmission

Posting Komentar untuk "Is Marburg Virus Zoonotic"