What Cells Does The Marburg Virus Attack
Known as virions these virus particles need to get back into cells to continue their lifecycle. They discovered that the receptor for this coronavirus is abundantly expressed in certain progenitor cells.
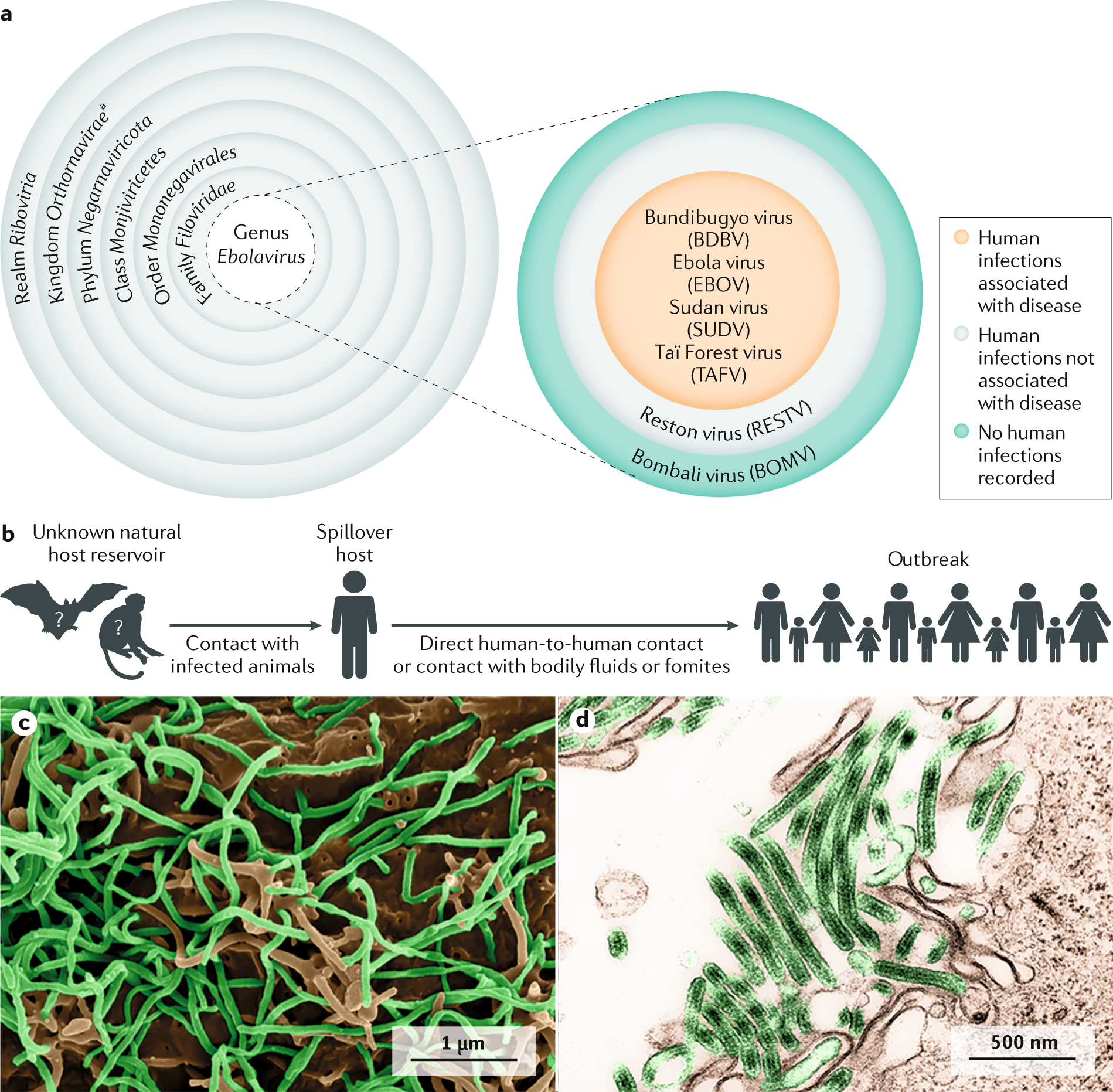
Ebola Virus Disease Nature Reviews Disease Primers
That cathepsin B and cathepsin L can individually cleave Ebola virus GP1 to yield an.

What cells does the marburg virus attack. Our data support the concept that the destruction of endothelial cells resulting from Marburg virus replication is a possible mechanism responsible for the hemorrhagic disease and the shock syndrome typical of this infection. Basler explained that Keap1 regulates the antioxidant response. The most recent outbreaks of Marburg virus disease have occurred in Uganda.
They showed that glycoprotein-mediated infection is substantially reduced in cells lacking these proteases. Scientists collect bats in Python Cave and attach GPS units on the backs of these bats to capture their movements to better understand how the Marburg virus is spread to people. Using existing data on the RNA found in different types of cells the researchers were able to search for cells that express the two proteins that help the SARS-CoV-19 virus enter human cells.
As will be discussed it seems that EBOV and MARV relentlessly infect cells of the monocytemacrophage lineage accelerating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumour-necrosis factor TNF. By fighting the virus the adaptive immune system selects and proliferates the B- and T-cells which are specific to the virus and so B-cells can label the cell-free virus in the blood with antibodies for destruction while T-cells can kill already infected cells. Proteins on the outside of the capsid interact with proteins on the outside of the cell.
They found subsets of cells in the lung the nasal passages and the intestine that express RNA for both of these proteins much more than other cells. They do this by attaching to molecules on the cell surface. It is unknown how Marburg virus first transmits from its animal host to humans.
Filoviridae contain one negative-sense RNA strand and have a covering or envelope composed of a lipid membrane. The case fatality rates CFR reported in the various outbreaks range from 24 to 100. The filoviruses most commonly associated with causing human disease are MARV and Ebola virus formerly known as Ebola Zaire EBOV 22.
This Review explores recent findings in the filovirushost-defence. Ebola and Marburg viruses MARV are members of the Filoviridae and induce a serious hemorrhagic disease. These cells normally develop into respiratory tract cells lined with hair-like projections called cilia that sweep mucus and bacteria out of the lungs.
The reasons seem to reside in a complex series of interrelated viral and immune events. As with some viruses but in a matter of days BOX 1. We show here that Marburg virus replicates in endothelial cells almost as well as in monkey kidney cells commonly used for virus propagation.
The disease Marburg virus causes is termed Marburg virus disease. After this initial crossover of virus from host animal to humans transmission occurs through person-to-person. Our study shows that Marburg virus VP24 interacts with the host protein Keap1 Dr.
The studys lead author Research Associate Shridhar Bale explains that a key signature of Marburg virus infection is the double-stranded RNA that results from its replication inside cells. However for the 2 cases in tourists visiting Uganda in 2008 unprotected contact with infected bat feces or aerosols are the most likely routes of infection. CDC scientists have spearheaded a small pilot project deep inside the forests of Uganda to track the movement of bats that carry the deadly Marburg virus a close cousin to Ebola.
Both families contain an RNA strand coated with proteins but the rhabdoviruses are more structurally homogenous which makes them easier to. Marburg and Ebola are the only two identified viruses that make up the small family of filoviruses a relative of the larger family of rhabdoviruses. The filoviruses Ebola and Marburg use several different and effective mechanisms to both evade and battle the immune system.

Ebola Virus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Ebola Virus Life Cycle 1 Ebov Gains Cell Entry By Receptor Mediated Download Scientific Diagram

Pin On Hemorrhagic Fevers Ebola Marburg Reston Lassa

Ebola Virus How It Infects People And How Scientists Are Working To Cure It Science In The News
The New Vision Infographic How The Ebola Virus Attacks The Current West African Outbreak Has Killed 48 Of Those Infected Facebook
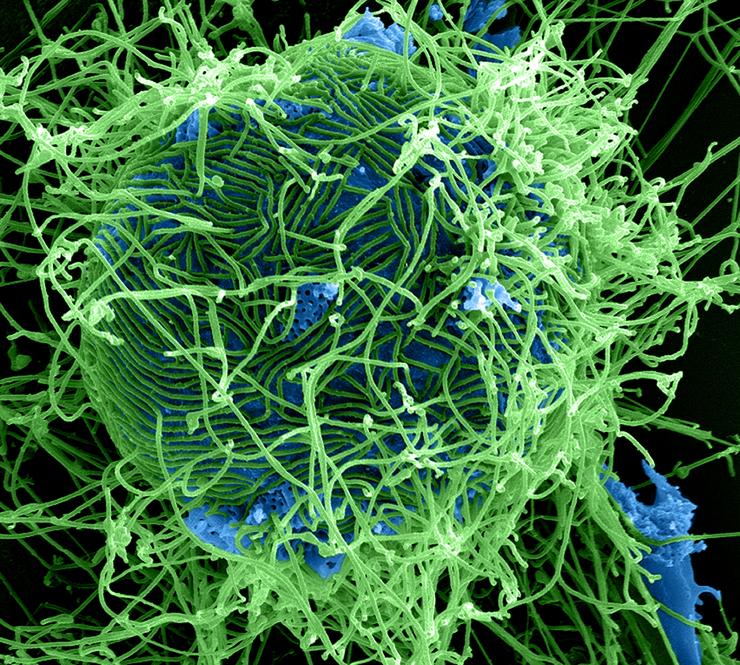




Posting Komentar untuk "What Cells Does The Marburg Virus Attack"