Marburg Virus Replication Cycle
Reverse genetics systems established for MARV have been used to study various aspects of the viral replication cycle analyze host responses image viral infection and screen for antivirals. Messenger RNAs gene order and regulatory elements of the replication cycle Heinz Feldmann 1 Elke Mlberger 1 Anke Randolf 1 Christiane Will 1 Michael P.
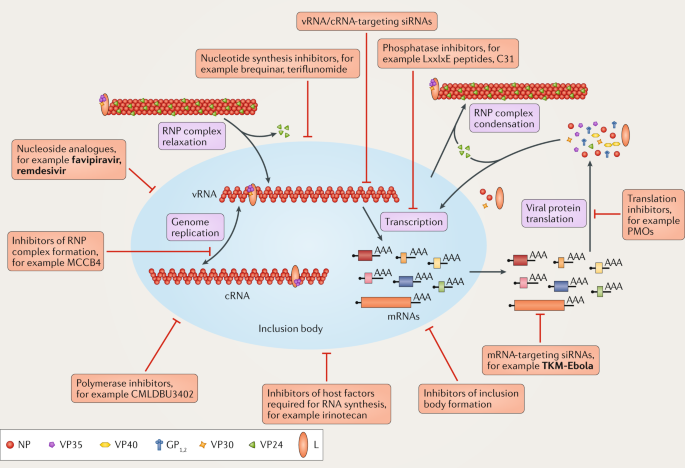
Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology
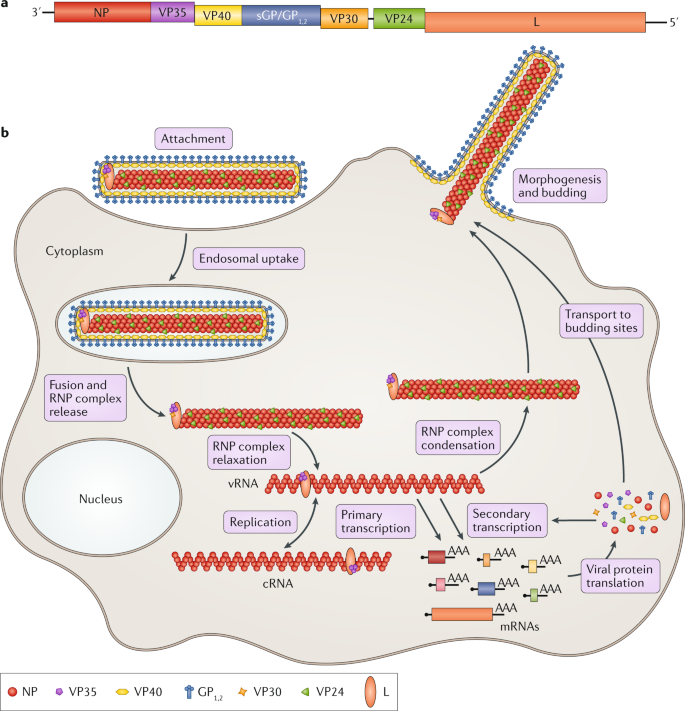
The replication cycle of filoviruses is complex and involves several viral and host proteins and cellular processes.
Marburg virus replication cycle. Replication of Marburg virus in human endothelial cells. The pathogen was named Marburg virus after the city with the most cases and represented the first isolation of a. The incubation period interval from infection to onset of symptoms varies from 2 to 21 days.
Muscle aches and pains are a common feature. MVD is a viral hemorrhagic fever VHF and the clinical symptoms are indistinguishable from Ebola virus disease EVD. Minigenome systems The filovirus genome consists of a single RNA strand in negative orientation and is tightly associated with 4 viral proteins the nucleocapsid proteins NP VP35 VP30 and L.
Illness caused by Marburg virus begins abruptly with high fever severe headache and severe malaise. Kiley 2a Anthony Sanchez 2 and Hans-Dieter Klenk 1 Institut fuer Virologie Philipps-Universitaet Marburg FRG and 2 Special Pathogens Branch. The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase transcribes genes into positive-stranded mRNAs which are later translated into structural and other proteins.
Marburg virus a filovirus. Replication cycle of filoviruses at and inside host cell The filovirus life cycle begins with virion attachment to specific cell-surface receptors followed by fusion of the virion envelope with cellular membranes and the concomitant release of the virus nucleocapsid into the cytosol. Translation is switched over to replication when viral protein levels rise.
Symptoms of Marburg virus disease. Viruses 2012 4 1879 of scientists in Marburg and Hamburg 2 and was later confirmed by Kunz and colleagues 3 and Kissling and colleagues 4. One of the key features of this replication cycle is the means by which nascent virions exit the host cell in order to infect new cells and ultimately spread to new individuals.
Once the Marburg virion attaches the virion envelop fuses with the cellar membrane and then the nucleocapsid is released into the cytosol. Viral RNA is then translated by employing the hosts mechanisms. Méssenger RNAs gene order and regulatory elements of the replication cycle Anthony Sanchez Received 22 October 1991revision received 12 December 1991accepted 13 December 1991 SummaryThe genome of Marburg virus MBG a filovirus is 191 kb in length and thus the largest one found with negative-strand RNA viruses.
Marburg virions attach to a host cell and enter through endocytosed vesicles. The final step of the viral replication cycle budding of the assembled virions is mainly driven by matrix protein VP40 via hijacking components of the cellular endosomal sorting complex required for transport ESCRT. Marburg virus disease MVD.
Marburg virus a filovirus. All rights reserved 0168-170292S0500 VIRUS 00752 Marburg virus a filovirus. Messenger RNAs gene order and regulatory elements of the replication cycle Virus Res.
The highly pathogenic Marburg virus MARV is a member of the Filoviridae family and belongs to the group of nonsegmented negative-strand RNA viruses. A possible mechanism for the development of viral hemorrhagic disease. Overview of the Marburg virus replication cycle including attachment and entry transcription and replication and viral budding and egress.
Reverse genetics systems established for MARV have been used to study various aspects of the viral replication cycle analyze host responses image viral infection and screen for antivirals. Messenger RNAs gene order and regulatory elements of the replication cycle. Formerly Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a severe illness of humans and non-human primates caused by either of the two marburgviruses Marburg virus MARV and Ravn virus RAVV.
When the virus membrane fuses with the vesicle membrane the nucleocapsid is released into the cytoplasm. Marburg virus a filovirus.

Schematic Diagram Showing The Replication Cycle Of Ebola Virus Ebov Download Scientific Diagram
Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology

Filovirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Typical Different Stages Of Virus Life Cycle 1 Attachment In Download Scientific Diagram

Filovirus Pathogenesis And Immune Evasion Insights From Ebola Virus And Marburg Virus Abstract Europe Pmc

Figure 1 From Filovirus Pathogenesis And Immune Evasion Insights From Ebola Virus And Marburg Virus Semantic Scholar

Marv Replication Cycle Marv Attaches To The Surface Of Target Cells By Download Scientific Diagram
Posting Komentar untuk "Marburg Virus Replication Cycle"