Characteristics Of Filoviridae Marburg And Ebola Viruses
Filoviruses belong to a virus family called Filoviridae and can cause severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and nonhuman primates. Marburg virus was first isolated during an outbreak in Europe in 1967 and Ebola virus emerged in 1976 as the causative agent of two simultaneous outbreaks in southern Sudan and northern Zaire.

Ebola Virus Life Cycle 1 Ebov Gains Cell Entry By Receptor Mediated Download Scientific Diagram
Six species of Ebolavirus have been identified.
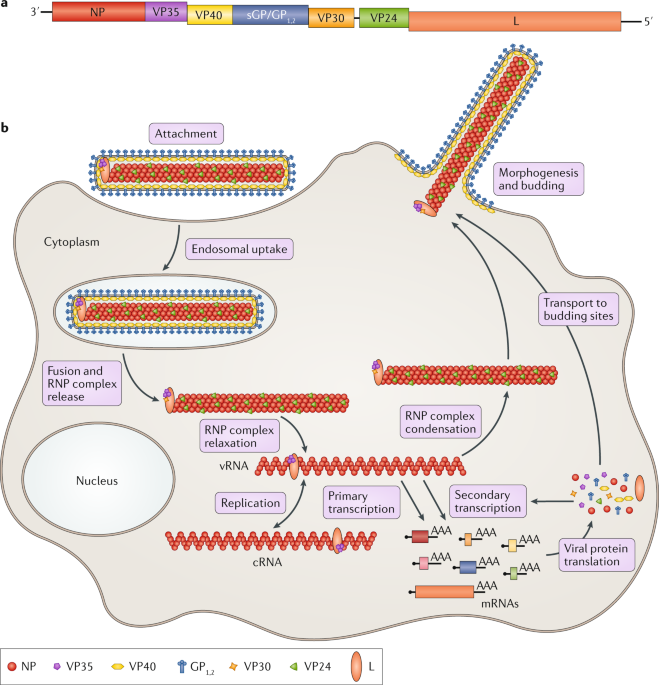
Characteristics of filoviridae marburg and ebola viruses. Marburg virus disease was first recognized in 1967 and is characterized by the same symptoms and transmission routes as Ebola virus disease. The filamentous viral particles of ebola- and marburgviruses contain a helical nucleocapsid that is enveloped by a host cell-derived membrane. Filoviruses are enveloped nonsegmented negative-stranded RNA viruses.
The Ebola and Marburg viruses are the sole members of the Filoviridae family of viruses. Marburg and Ebola viruses abstract Filoviruses are enveloped nonsegmented negative-stranded RNA viruses. Marburg and Ebola hemorrhagic fevers are severe systemic viral diseases affecting humans and non-human primates.
Ebola virus infection is slightly more virulent than Marburg virus infection. They appear to infect and persist in some species of fruit bats that may serve as natural reservoirs for these viruses 4 5 6 7 8 9. Filoviruses are enveloped nonsegmented negative-stranded RNA viruses.
Ebola virus isolates have been differentiated into 5 species. The two species Marburg and Ebola virus are serologically biochemically and genetically distinct. Ebola virus is part of the Filoviridae family which also includes Marburg virus.
Both viruses and some of their lesser known relatives cause severe disease in. Ebola- and marburgviruses cause a severe disease in humans. So far three genera of this virus family have been identified.
The two species Marburg and Ebola virus are serologically biochemically and genetically distinct. Paul-Ehrlich-Institute Paul-Ehrlich-Strasse 5159 D-63225 Langen Germany DE. Each virion contains a non-segmented negative-sense viral RNA genome.
They are characterized by a long filamentous form that is unique in the viral world. Filoviruses are among the most virulent pathogens currently known to infect humans. Marburg and Ebola viruses are zoonotic pathogens members of the Filoviridae family which cause severe often fatal illness in humans.
Brigitte Beer Reinhard Kurth. Two members of the family that are commonly known are Ebola virus and Marburg virus. Marburg and Ebola viruses are filamentous filoviruses that are distinct from each other but that cause clinically similar diseases characterized by hemorrhagic fevers and capillary leakage.
They are characterized by multiple symptoms such as hemorrhages fever headache muscle and abdominal pain chills sore throat nausea vomiting and diarrhea. Title Characteristics of filoviridae. Ebola viruses and Marburg viruses members of the filovirus family are zoonotic pathogens that cause severe disease in people as highlighted by the latest Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa.
Ebola and marburgviruses are members of the Filoviridae family. Filovirus disease is characterized by uncontrolled virus replication and the activation of host responses that contribute to pathogenesis. Filoviruses are among the most virulent pathogens currently known to infect humans.
The family Filoviridae a member of the order Mononegavirales is the taxonomic home of several related viruses that form filamentous infectious viral particles and encode their genome in the form of single-stranded negative-sense RNA. The viruses are members of the family Filoviridae a group of membrane-enveloped filamentous RNA viruses. The Ebola and Marburg viruses are the sole members of the Filoviridae family of viruses.
Laboratory of Infectious Diseases National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Bethesda MD 20892-0720 USA US. The two species Marburg and Ebola virus are serologically biochemically and genetically distinct. The Marburg virus and Ebola Zaïre Sudan and Bundibugyo subtypes have been associated with large viral haemorrhagic fever VHF outbreaks characterized by high person-to-person transmission and a case fatality rate ranging from 2590 whereas Côte dIvoire and Reston.
Marburg and Ebola viruses family Filoviridae genera Marburgvirus and Ebolavirus cause severe Viral Haemorrhagic Fever VHF in humans with a high fatality rate in symptomatic cases 123. There are two known species of Marburg virus that can cause disease in humans and nonhuman primates. Ebola virus species Zaire ebolavirus Sudan virus.
Marburg virus disease was first identified during an outbreak in 1967 when laboratory workers in Marburg and Frankfurt Germany and Belgrade Yugoslavia what is now Serbia were infected with a previously unknown infectious agent. They are characterized by a long filamentous form that is unique in the viral world. Cuevavirus Marburgvirus and Ebolavirus.
Infection with Marburg and Ebola viruses cause haemorrhagic fevers that are characterized by organ malfunction bleeding complications and high mortality.

The Ebola Virus Ebov Infects Multiple Organs A Variety Of Disease Download Scientific Diagram

Filovirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Ebola Virus Disease Nature Reviews Disease Primers

Ebola Virus Infection Etiology Bmj Best Practice Us

Ebolavirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Ebolavirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
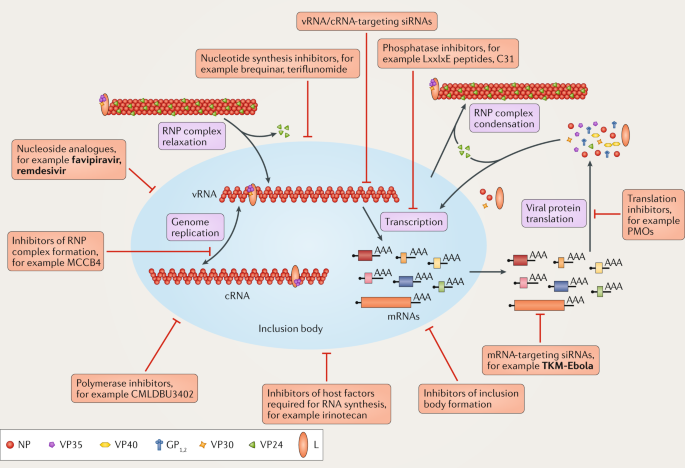
Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology

Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology

Ebola Virus How It Infects People And How Scientists Are Working To Cure It Science In The News

Filovirus Virus Family Britannica
Posting Komentar untuk "Characteristics Of Filoviridae Marburg And Ebola Viruses"