Marburg Virus Life Cycle
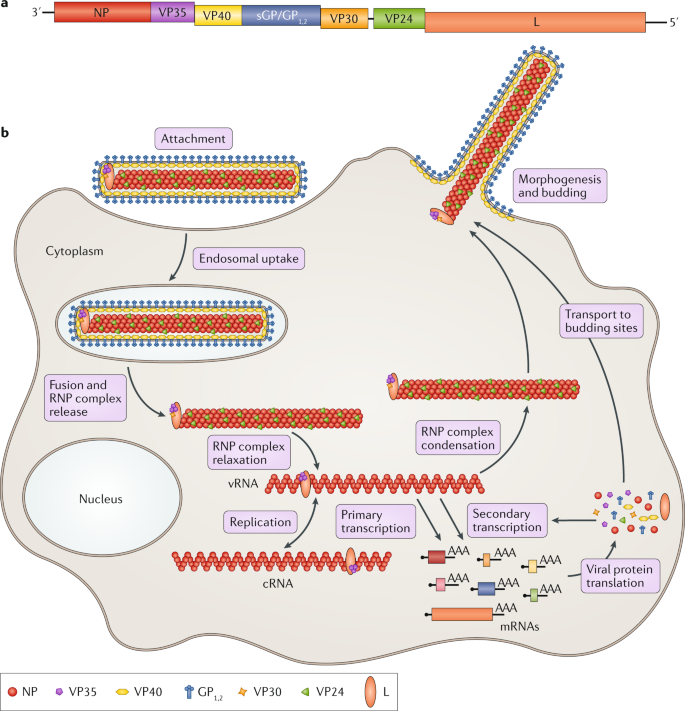
After this initial crossover of virus from host animal to humans transmission occurs through person-to-person contact. The marburg virus life cycle begins with virion attachment to specific cell-surface receptors followed by fusion of the virion envelope with cellular membranes and the concomitant release of the virus nucleocapsid into the cytosol.
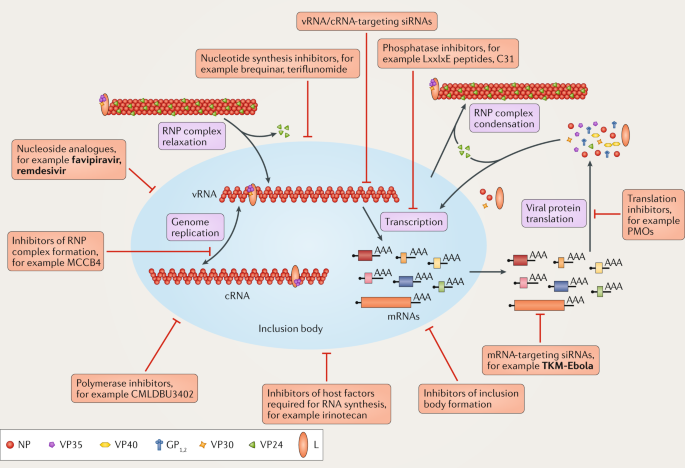
Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology
One-piece positive pressure ventilated suit with life support system is utilized.

Marburg virus life cycle. Using cryoEM the authors found that the host cells filopdia membrane extensions from which the virus buds could contain more than one nucleocapsid. The viral life cycle requires nucleocapsids to bud from the host cell membrane to form the infectious particle. People exposed to Marburg virus usually show signs of infection no later than about 14 days after exposure but because the clinical symptoms resemble Ebola virus disease most people are placed in isolation for 21 days.
However the virus does not survive for long periods after dying. Anywhere from 23 to 90 of people infected with the virus die from it generally about eight to nine days after symptoms first appear. Diagram of the life cycle of a Marburg Virus.
Symptoms usually appear 2 to 21 days after exposure and include sudden fever muscle pain headache and intense weakness. This may happen in several ways. Filovirus was first reported and named Marburg virus in 1967 during an outbreak of viral haemorrhagic fever HF in Frankfurt Germany and Belgrade Yugoslavia.
In many cases symptoms appear about a week five to 10 days after someone is infected with the virus 5 but they can come on anywhere from two days to three weeks. 4-5 days on contaminated surfaces longer in liquid. Information for Lab Workers Laboratory PPE.
In the lytic cycle the main cycle in viral replication once the viral DNA enters the cell it transcribes itself into the host cells messenger RNAs and uses them to direct the ribosomesThe host cells DNA is destroyed and the virus takes over the cells metabolismThe virus begins using the cell energy for its own use by creating copies of itself. However Marburg virus has been transmitted to primates by aerosol in laboratory experiments1 The disease is primarily spread through bodily fluids such as blood excrement saliva and vomit. Studying the replication cycle of the Marburg virus is done stepwise where versions of the virus that lack certain elements to stop them from becoming dangerous are used.
The average nucleocapsid contained over 3000 copies of the nucleoprotein arranged in a helix and each binding to six RNA bases of the viral genome in contrast VSV nucleoprotein binds nine RNA bases. Once all of the elements required to create a new Marburg virion the virus exits the cell via exocytosis and is then able to infect more of the hosts cells. In 1976 EBOV was determined to be the cause of outbreaks of viral HF in the Sudan and Congo.
Marburg virus MARV outbreak heamorhagic fever transmission origin life cycledeadly disease marburg viral disease prevention from outbreak t. The viral life cycle requires nucleocapsids to bud from the host cell membrane to form the infectious particle. Direct contact to droplets of body fluids from infected persons or contact with equipment and other objects contaminated with infectious blood or.
Marburg virus was first recognized in 1967 when outbreaks of hemorrhagic fever occurred simultaneously in laboratories in Marburg and Frankfurt Germany and in Belgrade Yugoslavia now Serbia. The marburgvirus life cycle begins with virion attachment to specific cell-surface receptors followed by fusion of the virion envelope with cellular membranes and the concomitant release of the virus nucleocapsid into the cytosol. Marburg virus disease is often fatal.
The incubation period is anywhere from five to ten days and early symptoms are often mild fever and headache. The illness progresses to a sore throat abdominal and chest pain vomiting diarrhea and a skin rash typically around the body trunk. Thirty-one people became ill initially laboratory workers followed by several medical personnel and family members who had cared for them.
In particular we address key stages of the virus life cycle that is entry viral RNA synthesis and morphogenesis and budding and discuss how both viral and host components involved in these.

The Typical Different Stages Of Virus Life Cycle 1 Attachment In Download Scientific Diagram
Therapeutic Strategies To Target The Ebola Virus Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology

Schematic Diagram Showing The Replication Cycle Of Ebola Virus Ebov Download Scientific Diagram
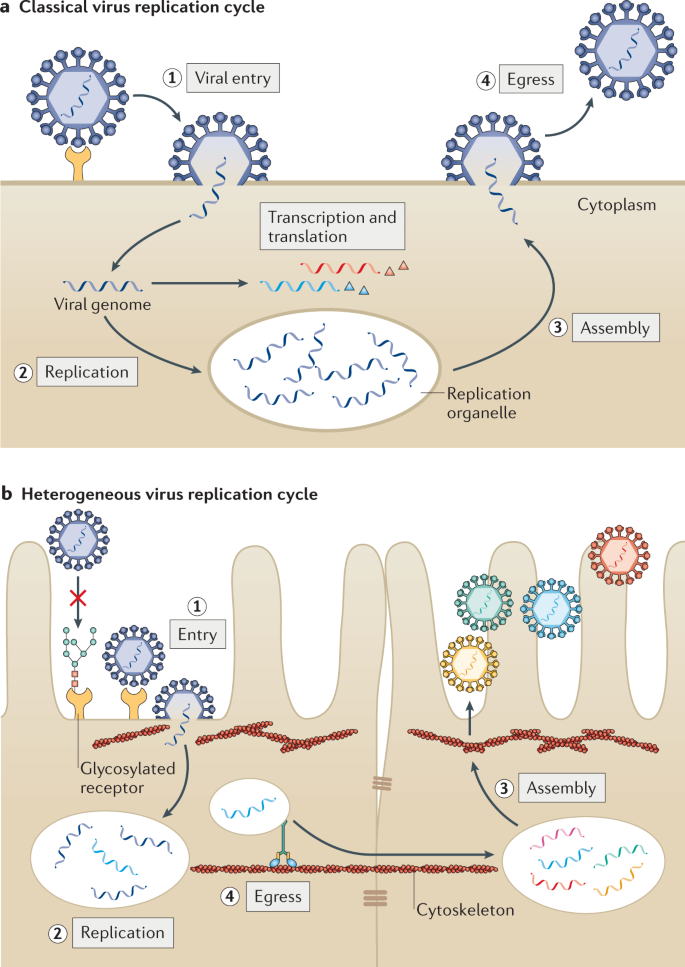
Viral And Host Heterogeneity And Their Effects On The Viral Life Cycle Nature Reviews Microbiology

Structural Rearrangement Of Ebola Virus Vp40 Begets Multiple Functions In The Virus Life Cycle Cell

Filovirus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Ebola Virus Life Cycle 1 Ebov Gains Cell Entry By Receptor Mediated Download Scientific Diagram
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Da Spostare

Figure 1 From Filovirus Pathogenesis And Immune Evasion Insights From Ebola Virus And Marburg Virus Semantic Scholar
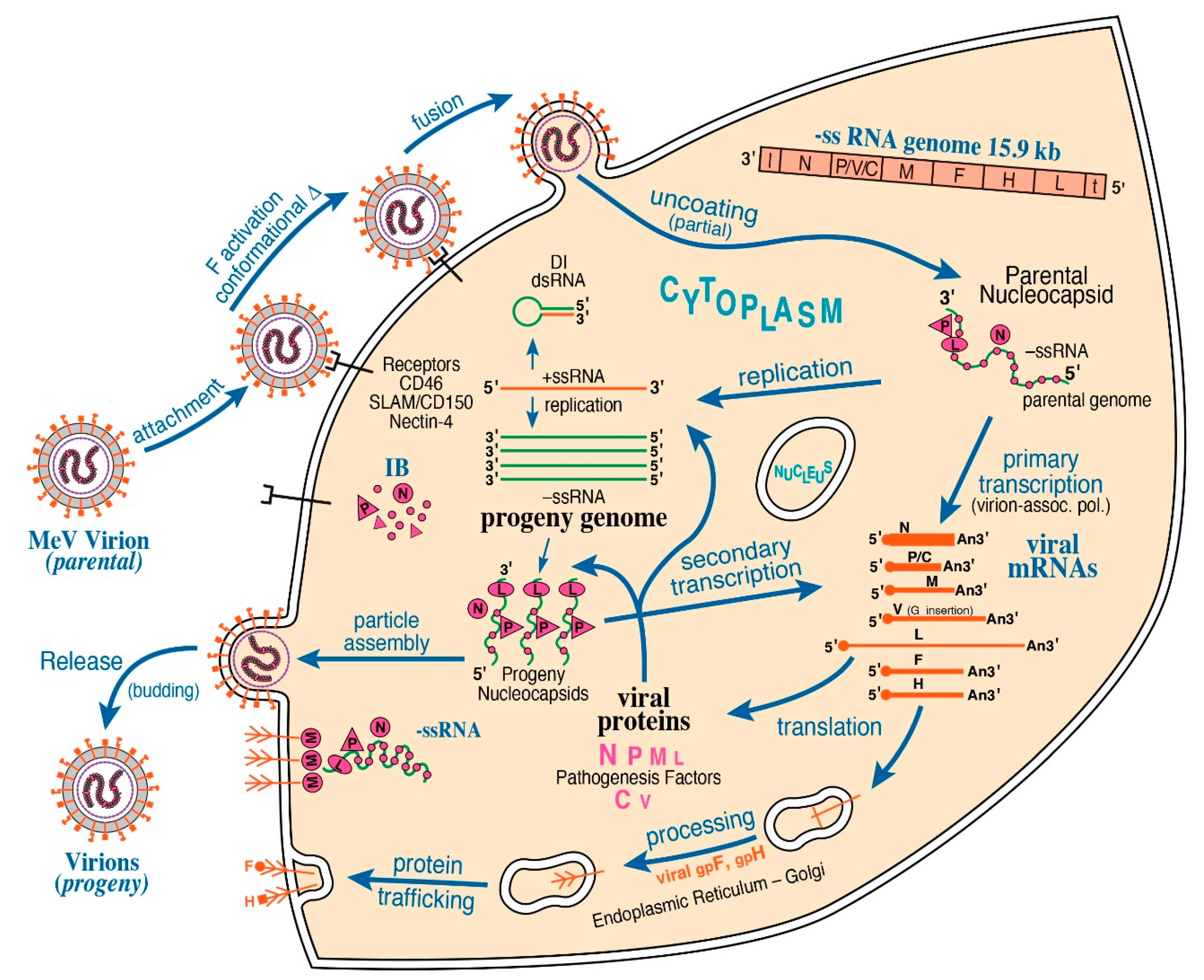
Viruses Free Full Text Formation And Function Of Liquid Like Viral Factories In Negative Sense Single Stranded Rna Virus Infections Html
Posting Komentar untuk "Marburg Virus Life Cycle"