Marburg Virus Etiology
Marburg hemorrhagic fever Marburg HF is a rare but severe hemorrhagic fever which affects both humans and non-human primates. The reservoir host of Marburg virus is the African fruit bat Rousettus aegyptiacus.

Marburg Virus Disease An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Marburg virus was first recognized in laboratory workers in Marburg Germany and Belgrade Yugoslavia in 1967.

Marburg virus etiology. The first documented outbreak of this disease was in 1967 in Germany and Yugoslavia which is currently known as Serbia. It has been isolated from bats and causes a similar syndrome to Ebola virus infection. These workers had been exposed to tissues and blood from African green monkeys Cercopithecus aethiops imported from Uganda.
It was detected in the blood urine throat-washing and seminal fluid. Ebola virus and Marburg virus are related viruses that may cause hemorrhagic fevers. MARV is a member of the Filoviridae family which consists of the genera Marburgvirus Ebolavirus Cuevavirus Striavirus and Thamnovirus 2 3.
Marburg virus MARV is the causative agent of Marburg virus disease MVD in humans with a case fatality rate ranging from 23 to 90 depending on the outbreak 1. These are marked by severe bleeding hemorrhage organ failure and in many cases death. Marburg virus can spread from animals to humans as well as from person to person and through contaminated objects.
Marburg HF is caused by Marburg virus a genetically unique zoonotic or animal-borne RNA virus of the filovirus family. 16 rows Marburg virus see the image below named after the German town where it first was reported in 1967 is another highly pathogenic member. Both viruses are native to Africa where sporadic outbreaks have occurred for decades.
Samples from the other 6 patients 66 were negative by virus detection methods and antibody testing suggesting another etiology. Fruit bats infected with Marburg virus do not to show obvious signs of illness. Marburg virus disease also known as Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a severe illness with a high mortality rate.
Our results reveal the most pathogenic MARV strain to be Angola followed by Musoke whereas Ozolin is the least. The five species of Ebola virus are the only other known members of the filovirus family. The pathogenesis and epidemiology of the Marburg-virus infection.
Shu HL Siegert R Slenczka W. Specimens from all 3 patients with Marburg infection were positive in all 3 assays. Marburg mahrʹboork Virus In August and September 1967 an outbreak of a viral hemorrhagic fever occurred among laboratory workers in Marburg and Frankfurt Germany and Belgrade Yugoslavia now Serbia who were processing kidneys from African green monkeys that had been imported from Uganda.
Africa eg Uganda Zimbabwe the Democratic Republic of the Congo 10 Contact with the reservoir host of the virus the African fruit bat. Several outbreaks have been reported often related to animal exposure in mines or caves. Monkey Diseases Virus Diseasesetiology.
Flaviviridae Dengue virus Dengue hemorrhagic fever. Primates including humans can become infected with Marburg virus and may develop serious disease with high mortality. Marburg virus disease is caused by the Marburgvirus single-stranded RNA virus.
Three of the 9 patients tested have confirmed Marburg virus infection by antigen testing virus isolation and PCR. In this study we compare the pathogenesis of Ravn virus RAVV and Marburg virus MARV strains Angola Musoke and Ozolin in rhesus and cynomolgus macaques the 2 nonhuman primate species most commonly used in filovirus research. Marburg and Ebola viruses both cause severe hemorrhagic fevers.
Ebola viruses and Marburg viruses members of the filovirus family are zoonotic pathogens that cause severe disease in people as highlighted by the latest Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa. The responsible pathogen Marburg virus is a member of the filoviridae family along with the Ebola virus. Marburg virus is the only other member of this group known to cause human infection.
Filovirus disease is characterized by uncontrolled virus replication and the activation of host responses that contribute to pathogenesis. Contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals or animals. Bat colonies body fluids or contaminated objects.
The virus affiliates with the immune system of the host which aids to determine the dynamics as to how the virus functions and affects the immune system. People are generally infected by Marburg virus after being exposed to one of three things. The aetiological agent was identified as an RNS-virus and was named Marburg virus.
Marburg virus Marburg hemorrhagic fever. Ebola virus and Marburg virus live in animal hosts. None internationally licensed.
5352745 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms.

Filovirus Pathogenesis And Immune Evasion Insights From Ebola Virus And Marburg Virus Abstract Europe Pmc

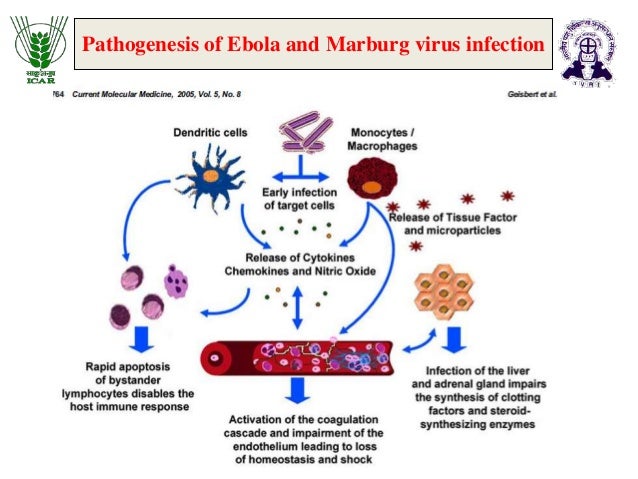
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Pathogenesis Model Download Scientific Diagram

Marburg Virus Origins Transmission Pathophysiology Symptoms Youtube

A Survival Curve Of Guinea Pigs Gps Infected With Marburg Virus Ravn Download Scientific Diagram

Establishment Of A Lethal Hamster Model For Marburg Virus A B Seven Download Scientific Diagram

Ebola Virus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Pathogenesis Model Download Scientific Diagram

Filovirus Pathogenesis And Immune Evasion Insights From Ebola Virus And Marburg Virus Abstract Europe Pmc
Posting Komentar untuk "Marburg Virus Etiology"